Dandruff is another name for a condition called seborrheic dermatitis. In this our scalp sheds skin cells in the form of yellow or white flakes. It’s very common in kids, teens and adults alike and is usually harmless. It it could be a little embarrassing especially for those who may already be self-conscious about their looks. In this article we are going to understand the cause behind these greyish flakes.
Due to dandruff you might even face problems like hair fall. For hair fall I have an amazing remedy for you <strong>5 HOME REMEDIES FOR HAIR GROWTH</strong>
Our skin cells are constantly replenishing themselves. In fact, every second 500 new skin cells are created and as they move up through the outer layer of your skin (the epidermis), they flatten out and harden until they fall off one by one. In fact, over your lifetime, you will shed about a hundred pounds of dead skin. But we don’t really notice this because skin falls off in such tiny microscopic pieces. Except for some people from some parts of the body skin comes off in larger flakes, typically from the skin under the hair the scalp. This is what’s known as dandruff. Now around half of everyone on earth suffers from it as long as you have hair.
Now the vital question is what is responsible for this head-scratching awkward condition?
Well for that we need to peek-a-boo into your head and look for a crawling creature a kind of yeast called Malassezia globose, living rent-free into your scalp surrounded by an abundant supply of food. Malassezia is a type of yeast that lives and dines on all of our scalps.
We might consider ourselves individuals, but we’re really colonies. Our skin hosts billions of microbes. Malassezia yeasts make themselves at home on our skin shortly after we’re born and its favourite room is the hair follicles. Follicles, the tiny cavities that grow hairs all over our body, make for especially popular living quarters. Malassezia are fond of these hideouts because follicles contain glands that secrete an oil called sebum. Sebum lubricate and strengthens our hair. Malassezia evolved to consume our skin’s proteins and oils. As our scalp is the oiliest spot on our body because of its many sebum secreting follicles. It makes a perfect breeding ground for these yeasts to thrive there.
MECHANISM OF MALASSEZIA GLOBOSE
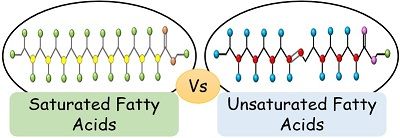
Sebum is composed of both saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. Saturated fats neatly pack together. Unsaturated fats, on the other hand, contain double bonds that create an irregular kink in their structure. But for some reason Malassezia likes to feed only on saturated fatty acids by secreting an enzyme that releases all of the oil’s fatty acids and leaving the unsaturated ones behind. These unsaturated fatty acids which are left, soak into the skin which opens its barrier allowing water to discharge out. The body immediately reacts to this discharge and activates the defence mechanism causing the inflammation that gives dandruff it’s itch. Then it activates the skin cells to reproduce for repairing the damaged barriers.

Usually, our skin’s outer surface, or epidermis, completely renews itself every two to three weeks. Epidermal cells divide, move outwards, die, and form the skin’s tough outer layer, which gradually sheds off in single cells far too small to see. But with dandruff, cells churn out quickly to correct the broken barrier, meaning they don’t mature and differentiate properly. So instead of taking a month for skin cells to mature and reach the surface they take as little as seven days. When they get to the surface the adhesive function from one cell to the other hasn’t been lost. So they shed as these clumps of skin cells three or four hundred together, which we see as a dandruff flake. This is how Malassezia’s voracious appetite and our body’s reaction to its by-products lead to dandruff.
But if everyone has Malassezia, why do some people have more dandruff than others?
Some people are more susceptible. Exactly why is unclear. Various factors increase the risk. It is not related to poor hygiene but it may be more visible if a person does not wash or brush their hair.
Different personal care products may cause contact dermatitis which makes your scalp red and itchy. Men develop dandruff more frequently than women. People who tend to have oily hair or live with certain illnesses such as Parkinson’s disease or HIV are also at higher risk.
What can we do to get rid of it?

Well, many cases of dandruff can be treated just by shampooing every day with a gentle anti-fungal shampoo. This will reduce oiliness and keep dead skin cells from building up. Look for shampoo containing one of the following ingredients pyrithione zinc, salicylic acid, selenium Sulphide. But remember not everything works for every person. So you may need to experiment until you find the one that works for You. If the problem persists, please visit your doctor.
INTRESTING FACT ABOUT DANDRUFF
Did you know you can get dandruff on your face and body too? Dandruff is not just limited to your Head but can grow on other areas of your body including the eyebrows, eyelids, ears, crease of the nose back of the neck, armpits, groin and belly button.
Conclusion
Scientists are investigating if there’s any benefit to our relationship with Malassezia. They hypothesize that dandruff, which can be uncomfortable and embarrassing for us, creates a reliable, oily food source for the yeast. But dandruff isn’t contagious or a great threat to our health. And Malassezia seem to excel at defending their territory which is our skin, from other more harmful microbes like Staphylococcus aureus.
So this was all about dandruff, if you have any questions, suggestions regarding the topic then do comment. For more such articles check out our website medicoved.com
Author : Dr. Easminara Shaikh


